|
First, I want to thank the Qualcomm Ventures team for inviting me to be a part of this amazing group of entrepreneurs, thought leaders, and innovators. The Edge AI Summit was among the best I have attended, and the hospitality of Qualcomm Ventures and the content were excellent and above board. The summit kicked off with a nice outside lunch in beautiful San Carlos, CA at The Alexandria and ended with an amazing dinner and drinks accompanied by a string assemble with beautiful, relaxing music. Now let’s jump into the summit highlights. Quinn Li, Senior Vice President and Global Head of Qualcomm Ventures, kicked off the event with a nice welcome message and set the stage for the overall theme, “Edge AI.” Bringing real-time data intelligence and insights for real-world industry solutions is vital, and artificial intelligence, learning models, algorithms, infrastructure, and security go hand-in-hand with the advancements and innovation. A range of early-stage and emerging companies that are partners and participants with Qualcomm Ventures are taking AI to the next level to apply to the enterprise and support adoption. Whether on-premise, on device, or at the point of data collection, AI is coming fast and Qualcomm Ventures will be leading and investing in the most innovative solutions in edge AI. One of the top highlights, was the fireside chat with Durga Malladi (SVP & GM, Technology Planning & Edge Solutions, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.) and Jim McGregor (Tirias Research), “Enabling On-Device AI.” The discussion focused on Qualcomm’s overall vision in AI. AI has been around since the 1950s and this past 18 months has shown good potential around generative AI in the most simplistic form. AI is primarily about intelligently connecting everything with the emerging use cases evolving around running generative AI on the device. Some of the use cases include voice and speech interaction, smartphones/laptops XR, advancements in consumer devices, and digital experiences in automotive. The convergence of communication and processing, while extracting meaning from it, gives rise to today’s AI and edge AI is an important component. AI and the processing of information is expected to run at an increasing rate purely on the device and not connected to the cloud. Inference training is happening at edge of the network, with action shifting from the cloud to a distributed manner or using a distributed architecture. With advancements in technology, large learning models are happening on the device and low power, efficient processing is supporting this trend. Qualcomm shares, “There is already a growing wave of sub-10 billion parameter large language models (LLMs), automatic speech recognition (ASR) models, programming models and language vision models (LVMs) that provide useful outputs covering a broad set of use cases.” As we move towards 5 to 10 billion parameter models on a device, the industry is building use cases with large language models (and other models) running on the device itself. The week of October 23rd was also the Snapdragon Summit, where Durga shared a couple of AI insights and “The Art of the Possible.” In addition to the increase in billions of parameters, Qualcomm also shared a range of companies (and their apps) and developer relationships to get us there including Google, LLaMA, and Hugging Face making sure all can run on Qualcomm devices. In addition, Qualcomm is focused on solutions to curate the model to make sure it runs efficiently on the device with proper compression, and not losing the sense of the model to retain accuracy. More developer tools will be made available to make sure the industry can ingest any model while also paying attention to the KPIs. Other key highlights include:
A More "Humane" AI was presented by Bethany Bongiorno, Co-founder and CEO of Humane and Imran Chaudhri, Co-founder and President of Humane. The leadership team formerly worked at Apple and decided to branch out and started their push into AI in 2019. Humane has 250+ employees working in San Francisco, New York, and in remote locations. Bethany and Imran presented on personal mobile computing and how it is driven by AI. They stated the slowdown in smartphone sales, and the OEMs are now looking for new areas of growth. They believe the future is NOT on your face. The future is the dynamic and contextual smartphone. Their unique technology brings the contextual computer and AI platform into an all-in-one phone, and stated they will be launching over the next few weeks. Imran and Bethany reference their TED talk where they share details around the role of contextual compute, a screenless, senseless, wearable device (on lapel) that uses gesture control. In fact, Naomi Campbell wore the device on the runway (reference article) at Paris Fashion Week in September. Their soon to be launched Humane Ai PIN is Humane’s first product and is a small form factor that resembles the “face” of a smartwatch but is worn or pinned to your clothing. The product is set to debut on November 9th. Next up was a fireside chat between Quinn Li and Tomer Weingarten, the Co-founder and CEO of SentinelOne. SentinelOne’s primary focus is based on the role of AI based security. SentinelOne shares they provide, “The First Security AI Platform to Protect the Entire Enterprise.” They leverage multi-modal AI learning that is predictive and integrated as the system should know what to do without asking. The solution is also aimed to know security risks before humans. The industry is shifting beyond the physical, and cracking integrated algorithms requires accuracy that we are missing today, shares Tomer. SentinelOne is pointing to very specific tasks and narrowing the scope as contextual AI is smart enough to figure out how to respond and predict. Tomer also shares that data sets are important as monitoring devices that ingest mass amounts of data, and even petabytes into the cloud is required to provide visibility and protection. SentinelOne has experienced 100% revenue growth in the last years reaching $1B annual recurring revenue (ARR). There were also two panels at the summit including one on AI infrastructure and one on warehouse automation. First, let’s share the highlights of the AI infrastructure panel titled, “AI Developer Tools & Infrastructure.” This panel was joined by Luis Ceze, theCo-founder and CEO of OctoML and Gourab De, Vice President of Weights & Biases. The panelists shared that some AI is disappearing because it is now part of the system i.e. decision trees, machine vision. In addition, compute cycles are being optimized for machine learning engineers and developers. Developers are now building products around the model, including uX ,and this means infrastructure needs to change fast with inferencing becoming more compute hungry and in real-time. Weights and Biases is using computer vision models to train the model faster, while collaborating with machine learning engineers and others. Generative AI requires new interactions and thought leadership including researchers, linguists, product managers and others. Some want to see things visually and prompt monitoring may need to be more visual and interactive. OctoML uses DeepAI while scaling, tuning, and running models in the cloud. AI developers require smarter tools and infrastructure to support large data sets, including media generation. “OctoML makes AI more sustainable through efficient model execution and automation to scale services and reduce engineering burden.” The second panel focused on Warehouse Automation and was the one that I personally had the privilege to moderate and participate in. Panelists included Arshan Poursohi, Co-founder & CEO of Thirdwave Automation, Lior Elazary, Founder and CEO of inVia Robotics, and Marcus Hehn, Co-founder and CTO of Verity. This session focused on robotics, autonomous systems, and drone technology used for supply chain management (SCM), inventory management, logistics, and warehouse operations. This session started out focusing on the industry challenges including visibility, real-time asset intelligence, and overall tracking and monitoring for optimal delivery of products and goods to the end customer. There are changing dynamics with companies like Amazon and others providing more customized and personalized customer experiences. This changing dynamic places greater need to leverage automation to manage inventory and assets. The panelists also shared insights on how machines and humans are working collaboratively. While robots and robotic systems can assist in repetitive and mundane warehouse operations, humans will have oversight and need to be trained to manage these systems. In addition, humans and machines will work together and education is important. Advancements in robotics and drone technologies, along with data intelligence gathering from these systems, is also giving rise to the acceptance in warehousing operations. The use of AI at the edge or data collection point is bringing real-time intelligence to many actionable insights specific to the products, inventory items, and delivery processes. The future of AI and the use with robotics, drones, and autonomous systems will revolve around data intelligence, machine vision, smart cameras, and large language model training. Two additional sessions including Deploying AI On Device presented by Krishna Sridhar, Co-Founder and CEO of Tetra and the fireside chat with Rahul Singh, the Co-founder and Vice President of Engineering at ideaForge provided additional insights around on-device AI and drone (UAS) mapping, security, and surveillance. In addition to the fireside chats, panels, and presentations, the summit also included fast-round “pitches” or quick insight sharing from the following companies:
Final Thoughts from Stephanie
The summit was hard-hitting, extremely insightful, and showcased a range of companies innovating and launching the next wave of technologies in Edge AI and enterprise automation. I find that the venture and young company competition events can be the best events to learn and open your mind to the “what’s next.” While my background is centered around technology, logistics, and automation, the wrapping of all three of these areas with advancements in AI is exciting and the industry will need to get it “right.” AI is extremely over-hyped and I evaluate the industry with caution. While generative AI overall has been targeted as being “free” and more consumer focused, the real opportunity lies around AI on device and AI in the enterprise. Just as with IoT and edge computing, it will be the AI solutions that address enterprise operations and provide true value that will win in the end. Value proposition, use case reliability, and industry-specific applications will be vital to bring AI to the “Art of the Possible.” Prepared and Written By: Stephanie Atkinson of Compass Intelligence On October 20th, a large group of industry analysts joined 5G Americas staff and members to discuss the state of 5G. Neville Ray of T-Mobile, Chair of 5G Americas, kicked off the event after a warm welcome and a setting of the stage by Chris Pearson (President of 5G Americas). Ray stated we are “In the next phase of 5G networks,” and “5G is finally starting to gain real traction.” A wide range of stats were shared along with some important factoids showing we are moving the needle in the Americas. Participating companies included Airspan, Cisco, Qualcomm, Samsung, T-Mobile, AT&T, Ciena, Mavenir, Nokia, Ericsson,Crown Castle, VMware, and Intel. While the foundational layer in 5G is located in the low band spectrum, mid-band 5G in the United States is now real…..but as all of us know, we need more mid-band spectrum to reach full potential of 5G use cases and applications. Currently, more than 66% of the geographic land mass is covered by 5G, while this same percentage of the population has access to 5G. Having a 5G enabled device is a bit underwhelming, with less than half of the U.S. population having access to a device with a 5G radio. With an investment of more than $100 billion over the last few years, 5G phones and subscriptions reached a total of 140 million, which remains less than half of the North American population. The most significant finding is that 5G is about increased data consumption, as Neville shared we are about 2.5 to 3 times higher data consumption with 5G compared to LTE. When thinking about the networks and advancements being made, we must remember we will rely on 4G/LTE for quite some time even though 5G networks are continuing to be deployed and improved. There are currently 14 total 5G networks running that enable streaming, gaming, social media and communications, and other business or enterprise-based applications. Outside of all of these data-intensive categories, Neville Ray mentioned for the industry to NOT forget about voice….yes, voice is still important for 5G and the advancements are really all around Voice over NR or New Radio (pronounced Vonar, aka Vo5G/Voice over 5G) (Related News: https://techblog.comsoc.org/2022/06/04/t-mobile-launches-voice-over-5g-nr-using-5g-sa-core-network/). 5G Americas noteworthy trends revolve around the following highlighted areas:
Fixed wireless access or FWA is being seen as an alternative to wired broadband and Wi-Fi (See Wi-Fi6) connectivity for a number of reasons. In many cases, the WISPs leveraged unlicensed spectrum to reach rural communities who lacked quality broadband, but over the past year the conversation has shifted to enterprise interest. Some believe it to be a complement or to augment existing connectivity options (especially cable). While FWA is creating capacity and new capabilities, especially for business use, additional and new spectrum is coming. FWA will continue to remain an available option for businesses in the US and internationally, but will continue to be squeezed by fiber and funding that may benefit fiber build out (Further Reading: WISPs embrace fiber as they face do or die moment). The carriers have been busy when it comes to FWA, especially in terms of their announcements and overall growth. Of course with that comes a bit of a reverse, as the overhype of FWA is now settling. “Verizon Communications…touted the addition of 234,000 fixed wireless access residential customers in the third quarter and another 108,000 FWA subscribers on the business-services side, upping its total FWA base to over 1 million users,” as seen on NextTV. T-Mobile will have their Q3 earnings call tomorrow but as Forbes shared, “T-Mobile has also made a dent in the broadband space, with its fixed wireless broadband offering adding an industry-leading 560,000 new broadband subscribers (last quarter),” while today they have more than 1.5 million FWA subscribers. Ericsson also shared, “UScellular was the first service provider to offer consumers and enterprise Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) services, using 5G extended-range millimeter-wave (mmWave) to target digital divide areas in rural America, reaching coverage of over 5 km.” While the activity for fixed wireless has expanded over the past year, spectrum access and fiber will remain critical factors for continued growth. Below is a slide that was shared at 5G Americas that highlights some of the overall FWA stats (Source: 5G Americas & Their Members). While some of you may be tired of tech acronyms, it is the way we lazy people essentially describe long-winded tech terms. Enter C-V2X or Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything). C-V2X is considered a mid-term opportunity and is expected to open up a range of opportunities driven by low latency, high performance 5G network services. Think about your car becoming your hub or essentially just like any other device. This hub will speak to the road, to traffic lights, to city traffic bodies, to public safety, to you and your passengers, to your auto dealership, to your car manufacturer and even to all your favorite content providers. In addition, these hubs will speak to each other building a network of communications across many sources. A range of entertainment, safety, location and routing, and interactive services will be launched and made available to drivers and passengers as a result. Your car needs reliable, high-speed wireless connectivity and 5G gets us there. We are in the earlier stages, but we do expect ongoing announcements well into 2023 to directly address the opportunities of 5G in C-V2X.
Network slicing is a near term focus across low, mid, and high-band spectrum. Enterprise and consumer applications focused on improved throughput, low latency, and other requirements see network slicing as a way to “carve out dimensional experiences,” shared Neville Ray. While we are in the early game of network slicing, we have yet to truly understand all the potential advantages and improvements that may come as we purpose-build the network. Aside from the key trends, and even more important, are the actual use cases for 5G. While the Analyst Forum had a strong emphasis on 5G for consumer and the growth in experiences there, I believe the true opportunity will lie with the enterprise and government sectors. Consumer 5G revolves around things like wearables, gaming, social communications, metaverse (not my favorite word), shopping, navigation, health/wellness, and sports. On the enterprise side, 5G presents new connectivity options for mass IoT and autonomous transportation, especially in use cases where the assets (fleets, products, equipment, people, machines, etc.) are mobile or meaning they are moving. These assets need to be monitored, measured, tracked, repaired, and acted upon for a variety of purposes and for reasons specific to the industry. Some of the vertical markets or industries where 5G opportunities exist include manufacturing, utilities, transportation, remote health care, digital cities, and education. For factories or logistics applications for example, mmWave is being used to enhance connectivity performance in robotics, as well as being used for sensing in agriculture or for farming applications. While 5G has been met with a sense of excitement and overall hype, we remain in the stage of improving overall network performance and build-out to meet enterprise and new customer experience expectations. There will always be hesitation for 5G adoption as a replacement to fiber, but for now we should think about applications where 5G is the only solution or where 5G will augment connectivity to provide better performance for things like robotics, transportation, supply chain monitoring, customer/digital experiences, etc. Lastly, the industry will continue to seek out additional mid-band spectrum as is needed to scale and to reach performance expectations. Special thank you to the 5G Americas team for hosting all of us analysts and for putting together great content. Contact Stephanie directly to learn more about other panel sessions and content that was shared at the event. Recommendations for further reading and research: Open RAN, Spectrum Policy and FCC Activities, mmWave, RedCap (Reduced Capacity) New Radio, Dynamic Spectrum Sharing, Unlicensed Spectrum. Please visit 5G Americas to learn more and to get access to their whitepapers and studies. To get access to further wireless research including 5G, please visit our WIRELESS RESEARCH store. Written by Stephanie Atkinson How Qualcomm is Advancing AI and Internet of Things to Prepare Tomorrow’s Businesses and Cities9/20/2022
In early July, I was honored to have a chat with Megha Daga, Senior Director of Product Management and AI/ML lead for the Internet of Things (IoT) at Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. . As a critical player in AI enablement across the IoT group at Qualcomm, Megha has been crucial in the development of cutting-edge AI solutions used around the world.
We dove right into what Qualcomm has been up to as it continues to advance IoT through the different core offerings, partnerships, and cutting-edge solutions that Qualcomm offers. To set the tone of our conversation, we discussed Edge AI. Edge AI is essentially intelligence moving to the data generator, according to Megha. Along with getting data faster, a host of other factors impact Edge AI, including privacy, cost, latency, reliability, and bandwidth. For businesses or enterprises, the simplicity of the technology revolves around business intelligence occurring on the device or close to the device itself to enable IoT. Qualcomm provides a portfolio of hardware technology, but even more exciting is their advancements in software design and embedded processing innovation. The company understands how heterogenous computing makes AI possible and is pushing the envelope to remain competitive in AI and IoT. Some of the stronger vertical markets and industries that Qualcomm is targeting include retail, logistics, energy, utilities, industrial, and robotics. To further advance into AI, Qualcomm launched the Vision AI Development Kit. This Azure IoT Starter kit is a vision AI developer kit for running artificial intelligence models on devices at the intelligent edge. With Edge AI, data is generated and pushed to the cloud. Legacy devices such as retail payment terminals and other industry specific devices are being digitized and modernized. Hardware or devices can be connected to a box, i.e., edge gateway. Megha shared that Qualcomm is taking metadata and compute to the box, implementing further compute as needed, then sending only the required data back to the cloud. The traditionally “dumb” environment is becoming more intelligent and bringing efficiencies to businesses and operations. Another Qualcomm AI example outside of retail is in logistics, more specifically warehouse operations. Robotics and drones may be used for picking and dropping, reducing overall payloads, and therefore reducing costs. Edge AI and IoT are coming together to minimize compute to the cloud, as the overall costs of sending massive data to the cloud is becoming more cost prohibitive, and a concern for larger enterprises. The issues of privacy, latency, and connectivity again remain important factors. Privacy not only affects consumers, it also impacts businesses and their customers’ experiences. As for latency, think of delivery robots on the street, providing sub-millisecond intelligence and information to enable operations and efficiency so consumers can get food, packages, products delivered (similar to same day delivery). Regarding connectivity, especially for operations in remote locations (construction, agriculture), having on-device or near device data intelligence can be critical. Examples Megha mentioned included drones connected to a gateway to enable crop intelligence, construction management, and mining operations. Qualcomm’s portfolio continues to evolve to support AI and Edge AI, with a stronger focus on software. Their hardware and chipsets will continue to be their foundation, as they grow their partnerships with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs). Qualcomm is leading in the areas of enabling AI on traditional CPUs/DPUs or AI on SDKs. Another cutting-edge development includes AI on embedded processing (low power, high performance). According to Megha, a few exciting AI areas that Qualcomm has been innovating around includes drone robots, and camera technology. Taking regular cameras for example and making them intelligent, using technologies such as machine vision and AI running on heterogenous computing to completely disrupt its capabilities. Megha shared that Qualcomm is using hardware accelerators for neural network workloads. Furthermore, AMR devices (autonomous mobile robots, i.e., Bosch devices) is an area where Qualcomm is developing chipsets and reference designs to further advance delivery. For example, they recently launched the RB6, a high-end chipset with an accelerator card allowing the robot to greatly improve throughput (i.e., delivery robots). As far as software goes, Qualcomm is investing and innovating to provide seamless software across the Qualcomm AI stack. Qualcomm is providing unification for developer building and changes, using Qualcomm Intelligence multimedia SDKs providing authentication and simplification for development and deployment, across multiple verticals. Developers and software tools remain a top priority for Qualcomm. Qualcomm realizes the end-customer (businesses and government) require and need end-to-end solutions and thus continues to build out its IoT partner portfolio (vendors, integrators, industry focused providers) focused on software/applications, platforms, and other solutions I’ll end with a great use case example shared by Megha. The Qualcomm AI Engine runs ML models in IoT devices, such as a security camera that recognizes a family member and activates a smart lock to allow entry. Or an office building that allows employees onto an elevator based on a touchpad. This context showcases the importance of how Qualcomm is advancing AI and IoT to prepare tomorrow’s businesses and cities. For more reading, please check out, “Qualcomm Advances Development of Smarter and Safer Autonomous Robots for Logistics, Industry 4.0, and Urban Aerial Mobility with Next-Generation 5G and AI Robotics Solutions” Written by Stephanie Atkinson, CEO of Compass Intelligence IN THIS EPISODE, STEPHANIE TALKS ABOUT THE HYPE BEHIND EDGE COMPUTING, THE FUTURE OF IOT, THE IMPORTANCE AND APPLICATIONS OF AUTOMATION, AND PROVIDES ADVICE FOR WOMEN WORKING IN TECHNOLOGY.
A week ago, I sat down virtually with Brandon Branham, Chief Technology Officer and Assistant City Manager of Peachtree Corners (PTC, one of the first cities in the United States powered by real-world smart city infrastructure, which also features ‘Curiosity Lab at Peachtree Corners’) to get an update on all of the progress being made in making the city smarter, more interactive, and inviting to technology innovators around the globe. Peachtree Corners launched an innovative living smart city lab about 1 year back that leverages autonomous technology, IoT, AI, machine learning, edge computing, virtual reality, and other advanced technologies to advance city operations, mobility, and introduce economic development. Some of the more interesting key facts about PTC include the following:
The innovation being embraced at PTC comes with the value it is placing in partnerships, leading technology company initiatives, and the live testing environment it provides to tech companies, OEMs, and startups around the globe. They currently have roughly 10 vendors with 15 different device types generating data across their network across around 15 or so different software systems. On the embracing of global companies, it is also working with a Tel Aviv company called IPgallery, that brings together city insights and intelligence using a real-time AI data platform that provides visualization (visual map) across PTC to monitor, analyze and secure all IoT devices across the ecosystem, buses, cameras, applications, etc. In addition, traffic flow and pattern data are being collected to adjust and make real-time rerouting decisions to improve public transportation.
PTC recently announced a partnership with Bosch, where they are implementing a sensor connected intersection and intelligent traffic management system to capture video including vehicle identification, vehicle recognition of objects (car, bus, scooters with drivers or without, pedestrians, etc. using machine vision). This partnership will allow real-time adjustments to traffic signaling, share the flow of traffic activity, and identify the type of vehicle in that flow for improved traffic management. PTC's Curiosity Lab will allow for a living city environment for Bosch to leverage its leading edge solution within a live, real municipality. A few other projects on the horizon include the following:
All of these activities would not be anywhere without the public-private partnerships (3Ps) in place. PTC has a process to test in their live environment, receive funding from 3rd parties or commercial entities (for some projects), decide on whether the project is scalable, and then the city decides and will invest as needed. This is a prime example of how business and government can and should work together to advance the smart city vision. On a final note, below is a list of key differentiators that enable PTC be the groundbreaking innovator in smart city solutions:
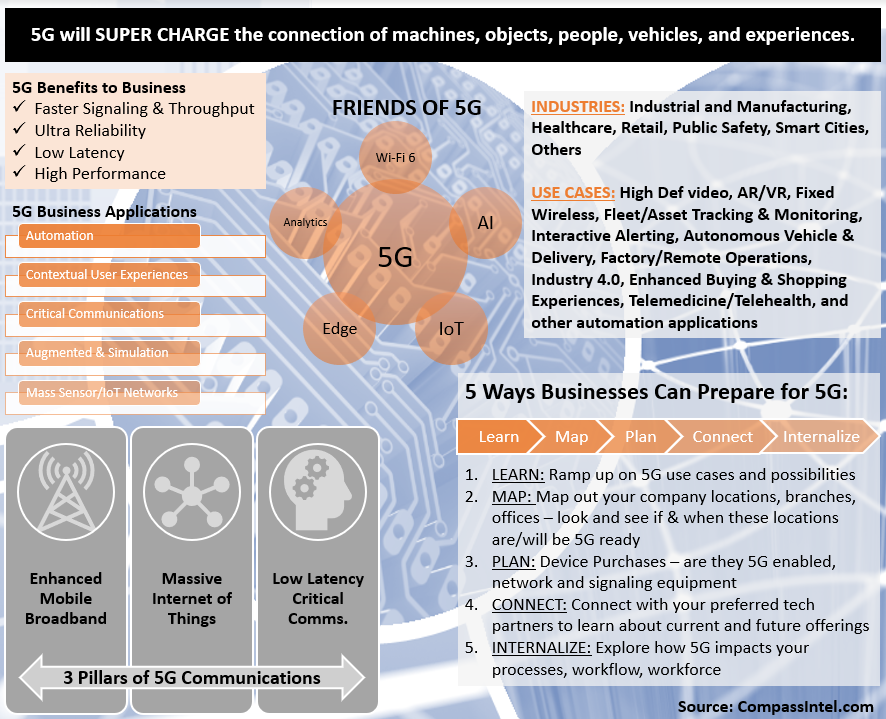
Platform There are two notable driving forces expected to bring significant change to the tech industry. First, we are at the emergence of 5G realization as networks are being upgraded and new devices enter into the market. Secondly, edge computing is taking over the past discussions of the cloud as the answer to bring analytics and insights in a real-time and automated manner. Let's skip the mechanics and deep tech discussion. Below are some basic thoughts around these two areas and why they are important to the future of work, smart cities, consumer entertainment, and much more. View the related 5G in Business Infographic below, podcast coming soon! CLICK TO DOWNLOAD NOW The Basics of 5G
As 5G networks are being launched in select cities, the industry is embracing new changes compared to 4G/LTE speeds. 5G brings the dawn of a new era where we connect machines, objects, people, cars, and more. The 5G infrastructure market brings new opportunities and potential applications that we have yet to unveil, and the industry is bracing for speeds that bring mass IoT to fruition, low latency critical communications that is ultra-reliable, and enhanced mobile broadband. Fixed wireless also becomes more of a reality across the nation, as 5G brings speeds that are expected to directly compete with cable and other high-speed Internet services. At this stage we are at the cusp of exploring new use cases, hard-hitting applications, and new device roll-out (smartphones launching middle of 2019 and some hotspot devices). Even more important is what this means to businesses, consumers, and even government customers. Businesses are expected to leverage 5G for industrial and supply chain automation, connected vehicle enhancements, massive 5G IoT enabled sensor networks and systems, and much more. Consumers will experience new entertainment experiences on their phones, cars, and in the home that bring speeds we have yet to experience, and content that bring new levels of entertainment. Governments will leverage 5G for critical communications, smart city applications, and new city services. The opportunities are endless and the market is prime to engage, learn, and explore what 5G brings to the world. The Basics of The Edge Edge computing is an explosive topic for the tech industry, as we push intelligence to network end-points and devices as opposed to pushing data to the core/centralized cloud or to a remote server/datacenter. Chipset technologies have advanced where data analytics and decisions are being made at the equipment or device for critical decision making, business process improvement, and important action enablement. Edge computing combined with Internet of Things, brings simplification and new possibilities for immediate and real-time decision making for things like fleet management, asset tracking, supply chain management, advance manufacturing, building management, and improvements to smart cities. Additional technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning solutions elevate automatic decision-making and are further executed to bring automation to new levels for businesses and government. Edge computing coupled with the convergence of AI and IoT (AIoT) will lead to “thinking” networks and systems that are becoming increasingly more capable of solving a wide range of problems across a diverse number of industry verticals. Additional benefits anticipated include creation of new customer experiences and improved consumer applications such as within the entertainment industry. RELATED RESEARCH: 5G Research Reports Edge Computing Research Reports |
Inside MobileCovering hot topics in the industry, new research, trends, and event coverage. Categories
All
|



























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed